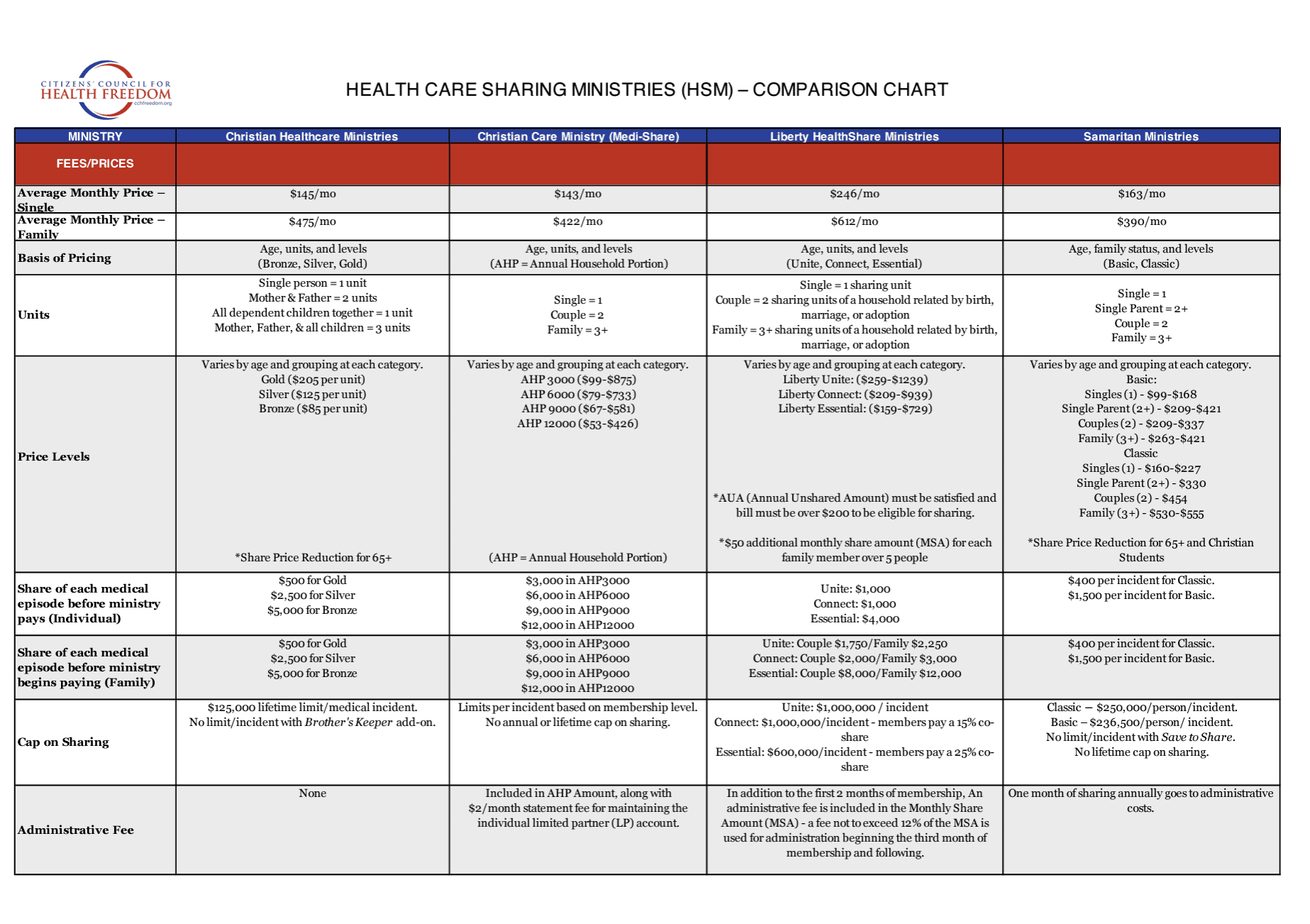
Publications
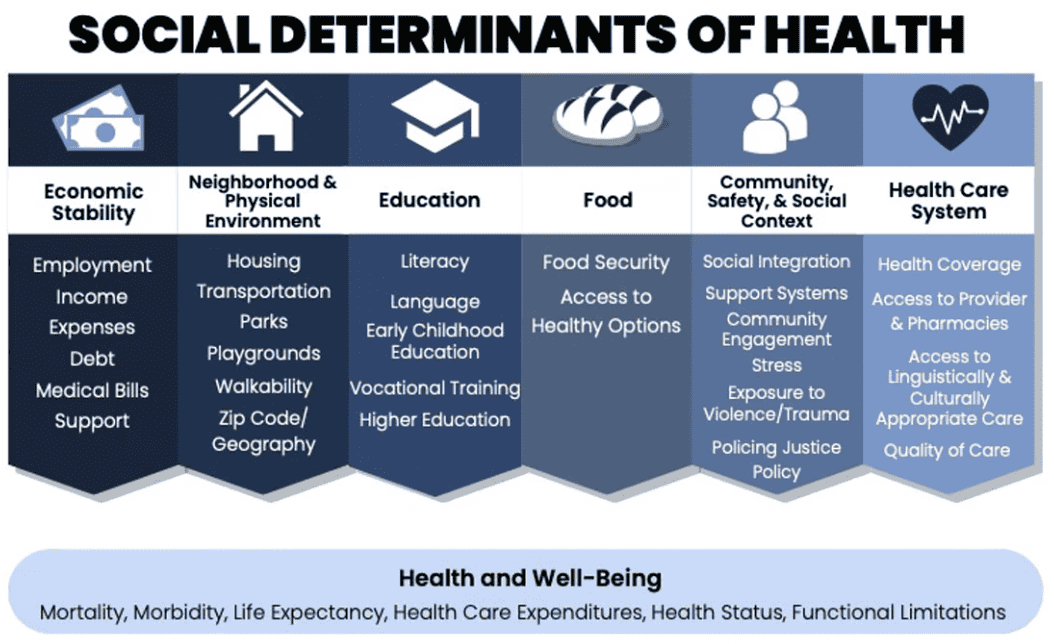
When it comes to fighting for health freedom, information is key and knowledge is power. You can find CCHF’s latest content – as well as our archived content – here on our website. From original papers and articles to issues of our quarterly Health Freedom Watch, this is where we add published content to keep you informed.

Key Initiatives
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Enter your email to begin receiving monthly newsletter emails.
Visited 3,986 times, 366 visit(s) today